Headings
On this page
- Headings for Jadu users
- Headings for WordPress users
- Headings for Word users
- Headings for SharePoint users
Overview
Headings (eg Heading 2, also known as an H2) enable you to structure and separate information. Each heading creates a new section.
Do not use a heading type if you only want to style the text.
What and why: Headings make it easier for users of assistive technology to skip to the information they need. Following the appropriate hierarchy makes the page more intuitive for all users.
Heading numbers
A higher heading number (eg Heading 2) indicates that it's a subsection of information under a lower heading number (eg Heading 1).
Headings typically get smaller in font size the higher the heading number to indicate hierarchy.
There should only be one Heading 1 (H1) on a page.
In Jadu, the H1 is typically set in the ‘Page Title’ field. In WordPress, this can be edited in the editor’s top title box. In both cases, the first header you set in your page’s body content should be an H2.
Sequence
Heading levels must only increase one step at a time. For example:
Heading 1 (H1)
Heading 2 (H2)
Heading 3 (H3)
You cannot skip one or more levels upwards. For example H1 to H3:
Heading 1 (H1)
Heading 3 (H3)
You can skip down any number of headings. For example H4 to H2:
Heading 1 (H1)
Heading 2 (H2)
Heading 3 (H3)
Heading 4 (H4)
Heading 2 (H2)
Return to the top of the page.
Headings before widgets/elements
It’s helpful if important or useful widgets or page elements in the body of a page, particularly tools or search boxes, are preceded by a heading. Describe the widget or page element in the heading.
What and why: Headings above important widgets or elements make it easier for users of assistive technology to skip to them.
Return to the top of the page.
How to
Headings for Jadu users
How to add headings in Jadu
- Highlight the text you want to make into a heading.
- On the formatting toolbar, go to the ‘Paragraph Format’ drop-down near to the buttons for ‘Bold’ and ‘Italic’.
- Select the heading level you require - the highlighted text will change to the format you have chosen.
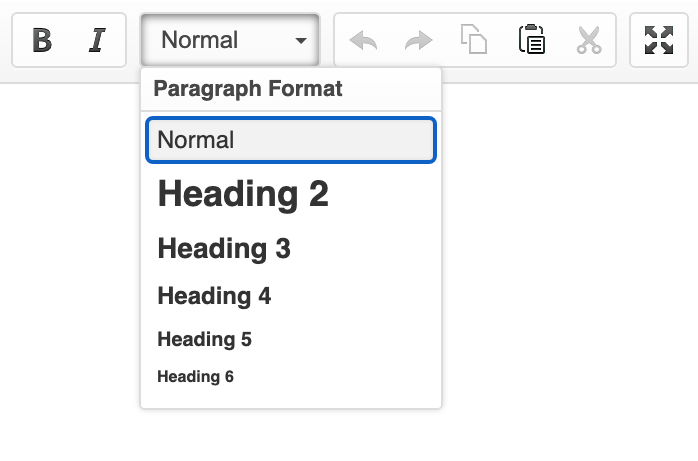
Return to the top of the page.
Headings for WordPress users
How to add headings in WordPress
- Highlight the text you want to make into a heading.
- On the editor toolbar, go to the ‘Paragraph’ drop-down near to the buttons for ‘Bold’ and ‘Italic’.
- Select the heading level you require - the highlighted text will change to the format you have chosen.
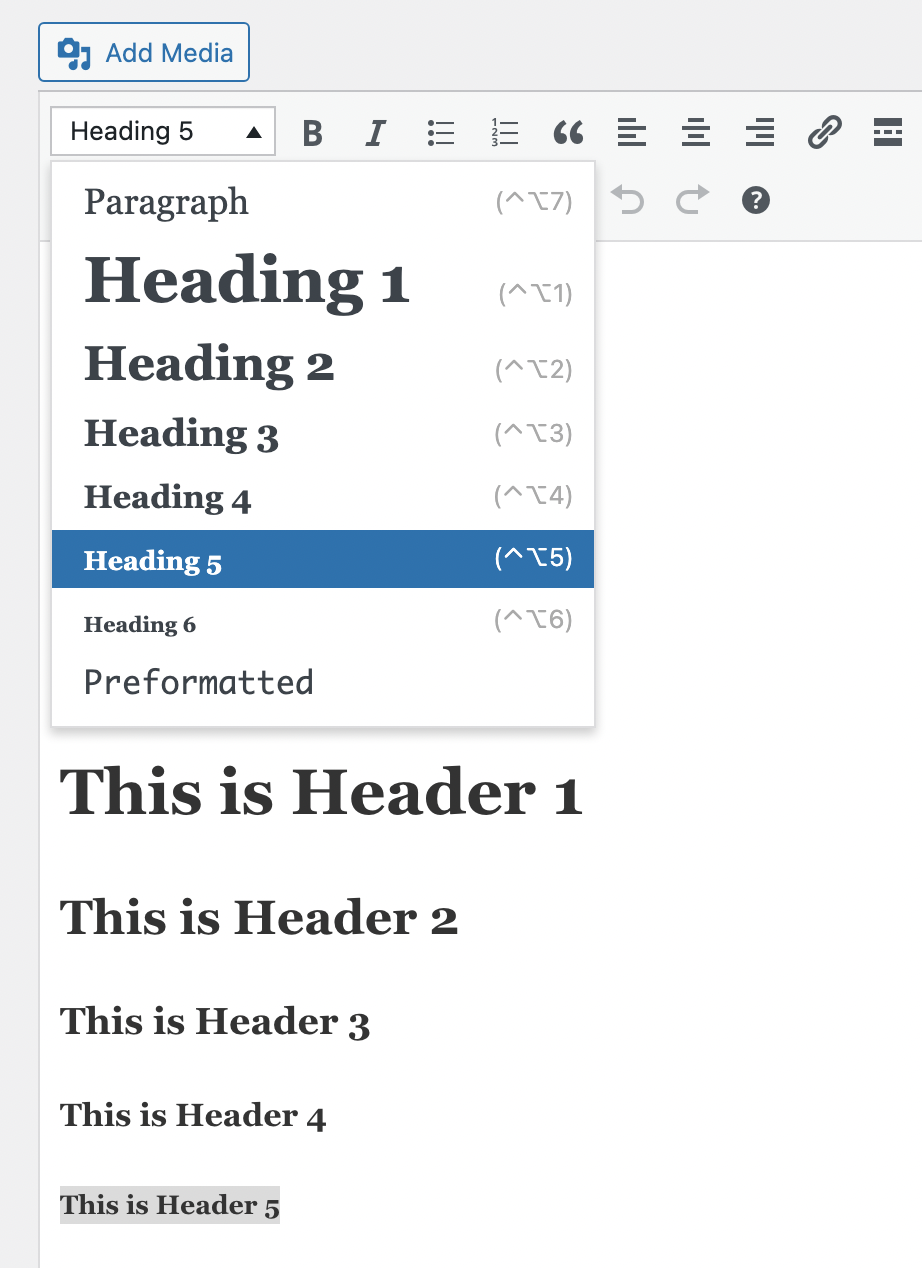
Return to the top of the page.
Headings for Word users
How to add headings in Word
- Highlight the text you want to make into a heading.
- On the ‘Home’ tab of the toolbar, go to the ‘Styles’ section.
- Select the style - the highlighted text will change to the format you have chosen. Use the following header sequence:
-
- ‘Heading 1’ for the document's title
- ‘Heading 2’ for the document's main section headings.
- ‘Heading 3’ for subsection headings.
- Heading 4, 5, etc for further subsections if needed.
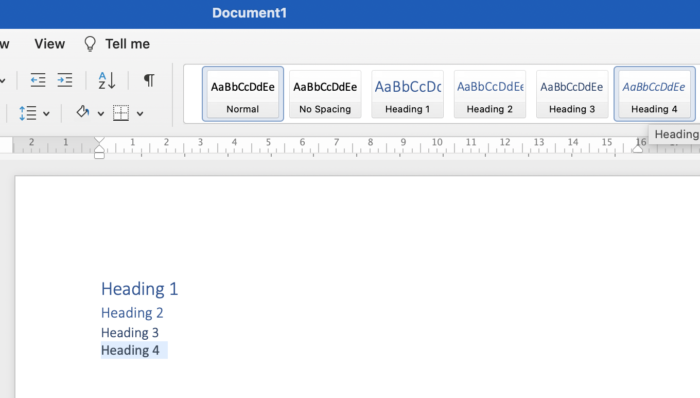
Return to the top of the page.
Headings for SharePoint users
Unlike the other examples on this page, SharePoint slightly adjusts heading levels after you've set them. Although it may seem counterintuitive, Microsoft drops your headings level down one step for end users.
For example, a Heading 3 will become a Heading 4 on the live page. Ensure that you take this into account; use Heading 1s for your main sections, Heading 2 for a subsection, and Heading 3 for your sub-subsections. These will change to Heading 2, 3, and 4 respectively when viewed by users.
